Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, relies on the use of probes or transducers to capture detailed images of the body's internal structures. These devices are pivotal in various medical fields, from obstetrics to cardiology, and choosing the right one is crucial for accurate diagnostics. In this guide, we'll explore the differences between ultrasound probes and transducers, delve into which probe to use for specific applications, and discuss the various types available in the market.
What Are The Ultrasound Probes?
An ultrasound probe, often interchangeable with the term 'transducer,' is a device that both emits and receives high-frequency sound waves. When these waves are directed into the body, they reflect off tissues and return to the probe, which then converts them into electrical signals. These signals are subsequently processed to create an image of the internal structure being examined.
Ultrasound Transducer vs Probe
While 'ultrasound probe' and 'ultrasound transducer' are terms commonly used to refer to the same device, it's important to note that a transducer is technically the component of the probe that converts electrical energy into sound waves and vice versa. However, in clinical practice, both terms describe the handheld instrument used during an ultrasound scan.
Choosing the Right Ultrasound Probe
The selection of the appropriate ultrasound probe is critical for obtaining the best possible image quality and ensuring a correct diagnosis. Factors such as the area of the body being imaged, the depth of the tissues involved, and the desired resolution all play a vital role in determining which probe to use. Here, we will outline the various types of probes and their intended applications to help you make the most informed choice.
Types of Ultrasound Probes
Ultrasound probes come in different shapes and sizes, each tailored for specific diagnostic purposes. Here's a quick overview of the most common types:
Convex (Curved) Probe: With a wide field of view, these probes are typically used for abdominal and obstetric imaging.
Linear Probe: These are ideal for imaging superficial structures like blood vessels, nerves, and muscles, providing high-resolution images.
Phased Array Probe: Small and versatile, these probes are perfect for areas with limited access, such as between the ribs for cardiac imaging.
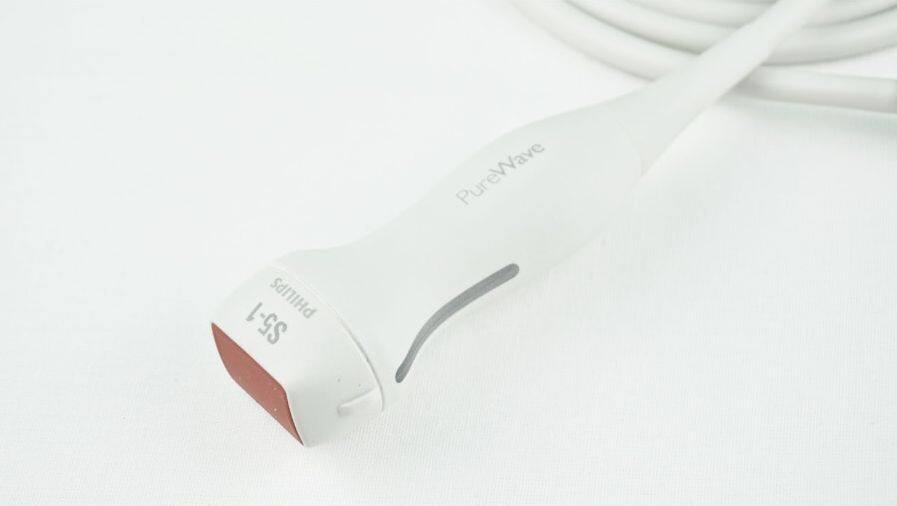

Philips S5 1 Ultrasound Transducer
Endocavity Probe: Designed for inserting into body cavities, these probes are used for transvaginal or transrectal imaging.
For a more comprehensive understanding of the different types of ultrasound probes and guidance on selecting the right one for your needs, consider reading our detailed article: "What Are The Different Types Of Ultrasound Probes?"
.
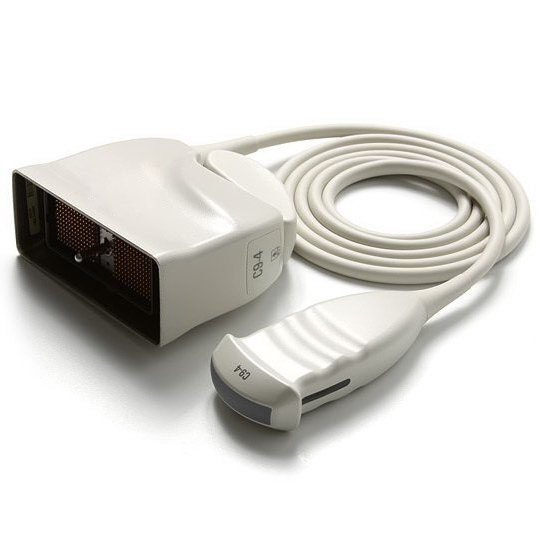

Evaluating Compatibility and Technology
Before selecting a probe, it's crucial to ensure it's compatible with your ultrasound system. Additionally, consider the latest advancements in transducer technology that could enhance your diagnostic capabilities, such as 3D/4D imaging or elastography.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate ultrasound probe or transducer is a nuanced process that significantly impacts diagnostic accuracy and patient care. By understanding the differences and applications of each type, you can make a choice that aligns with your clinical needs and budget. For more information on our range of ultrasound equipment, including ultrasound probes, reach out to Xity, your trusted ultrasound equipment supplier in China.
 English
English
 Русский
Русский